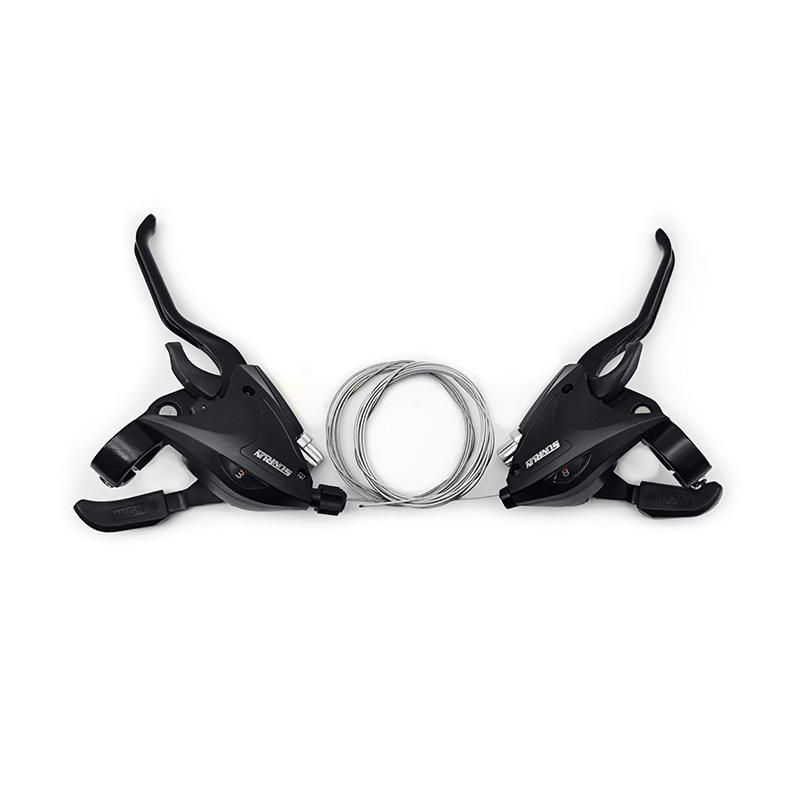
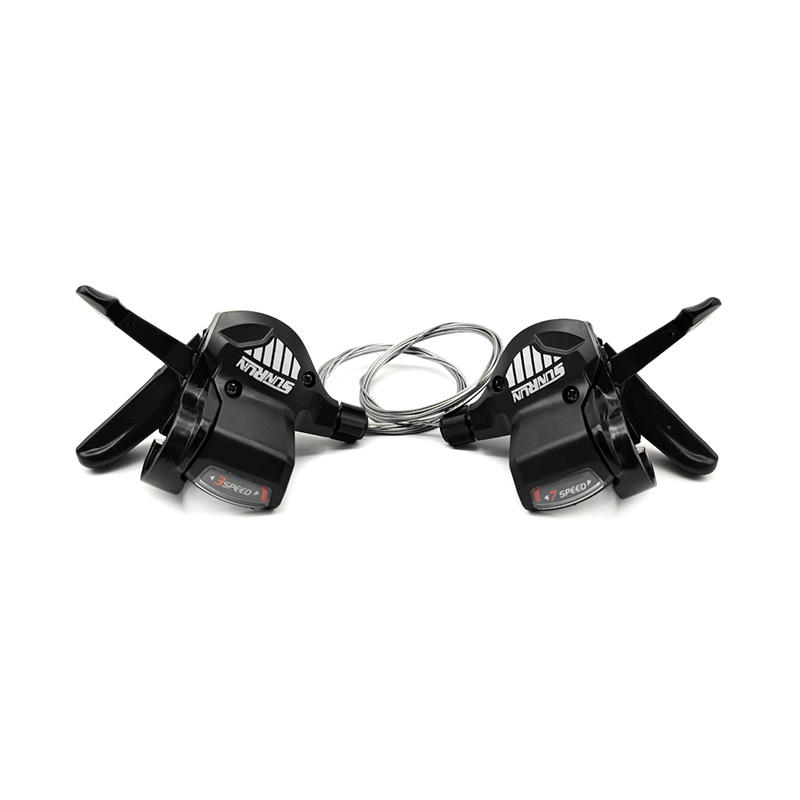
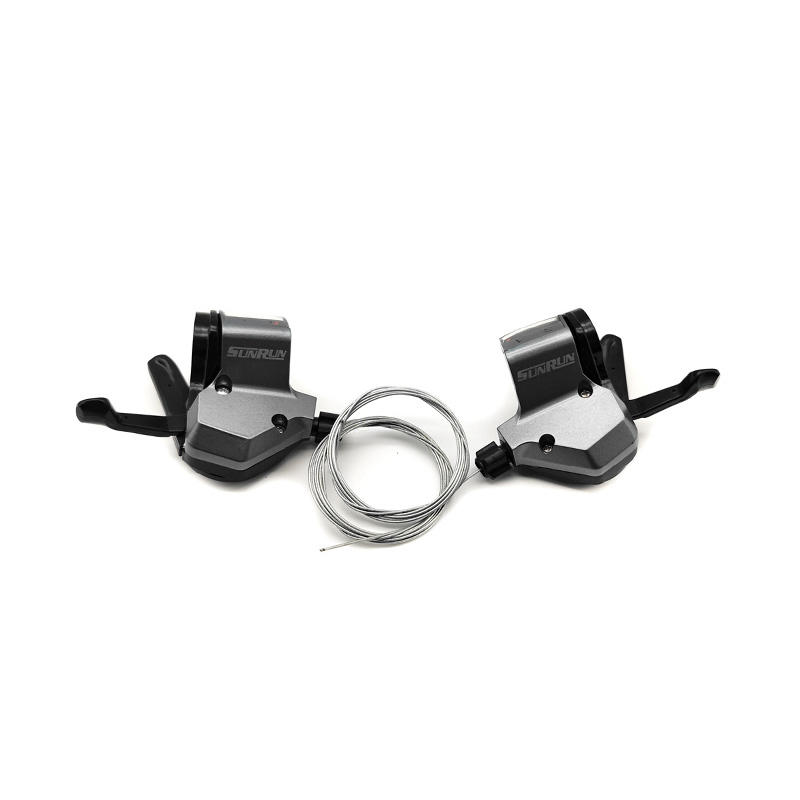
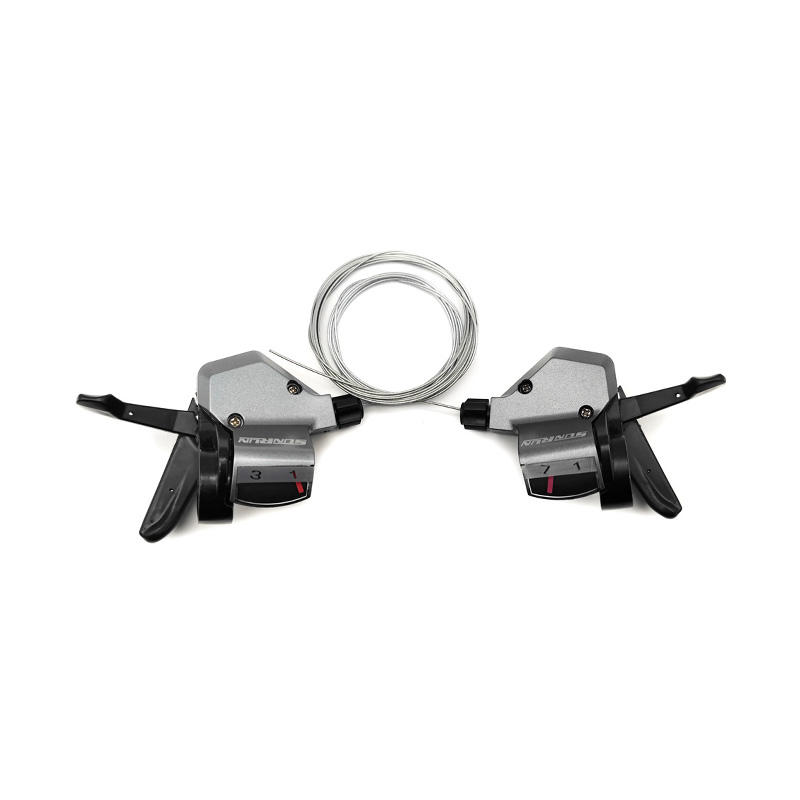
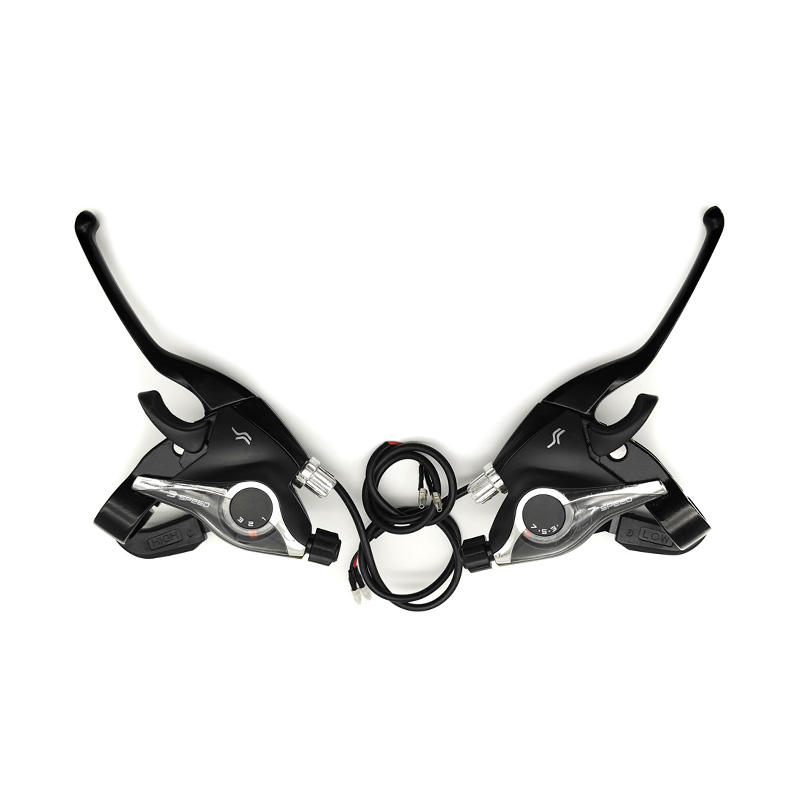
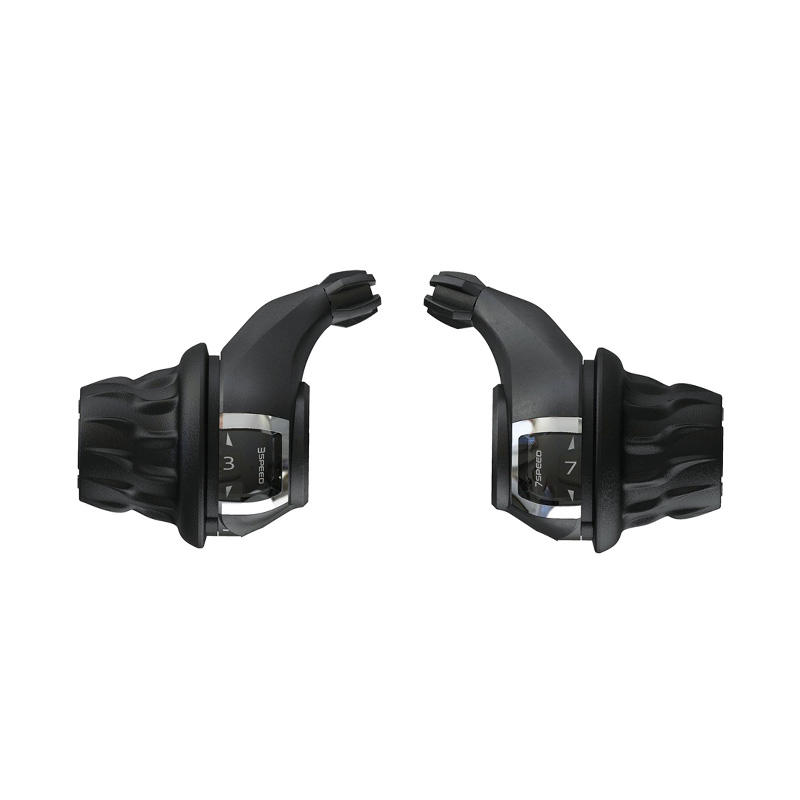
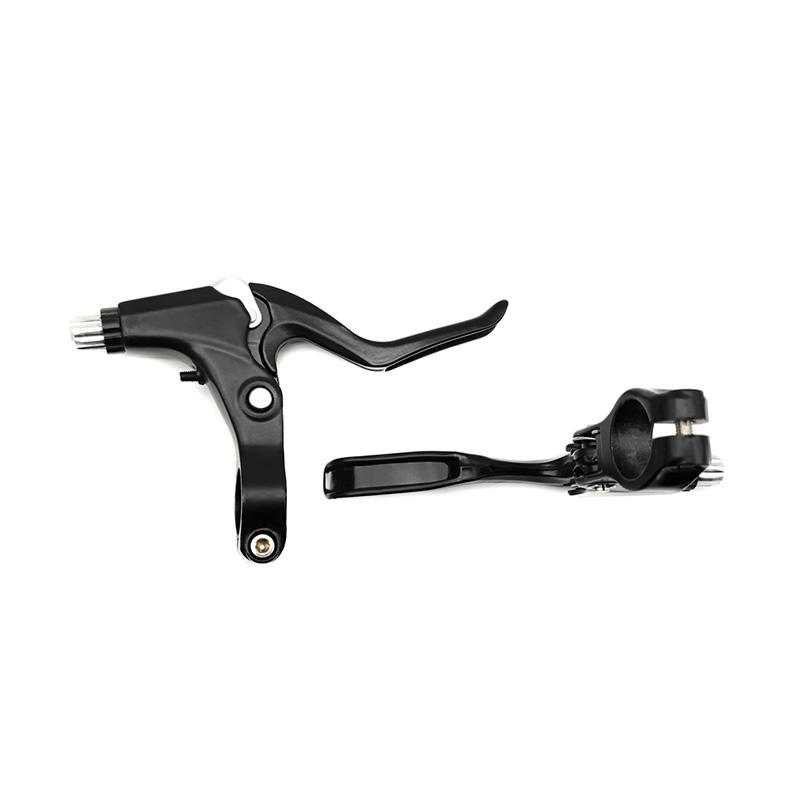
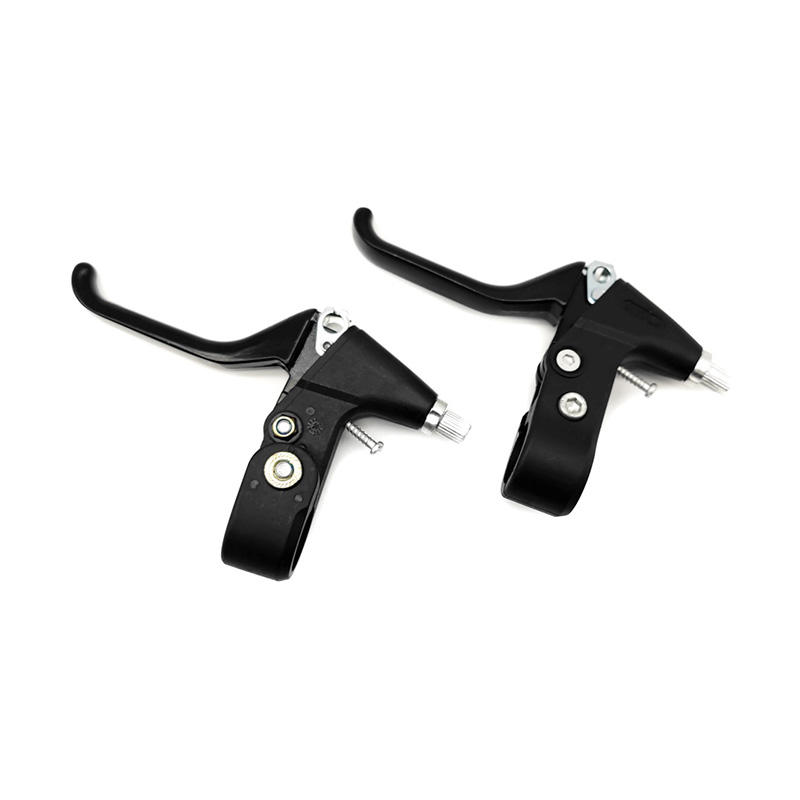
-
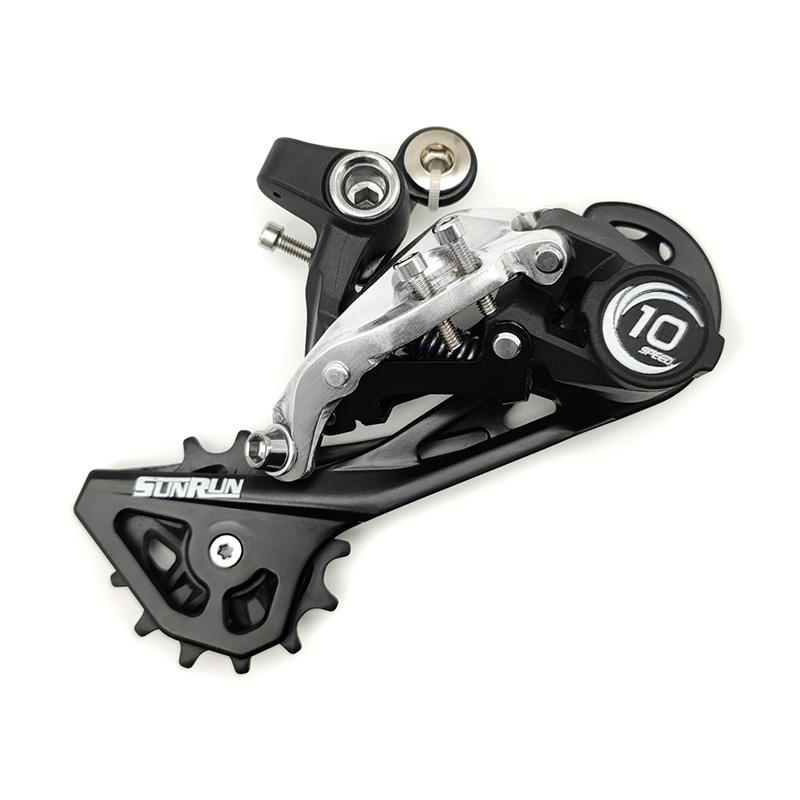
 What key role does the front derailleur play in the bicycle speed change process?
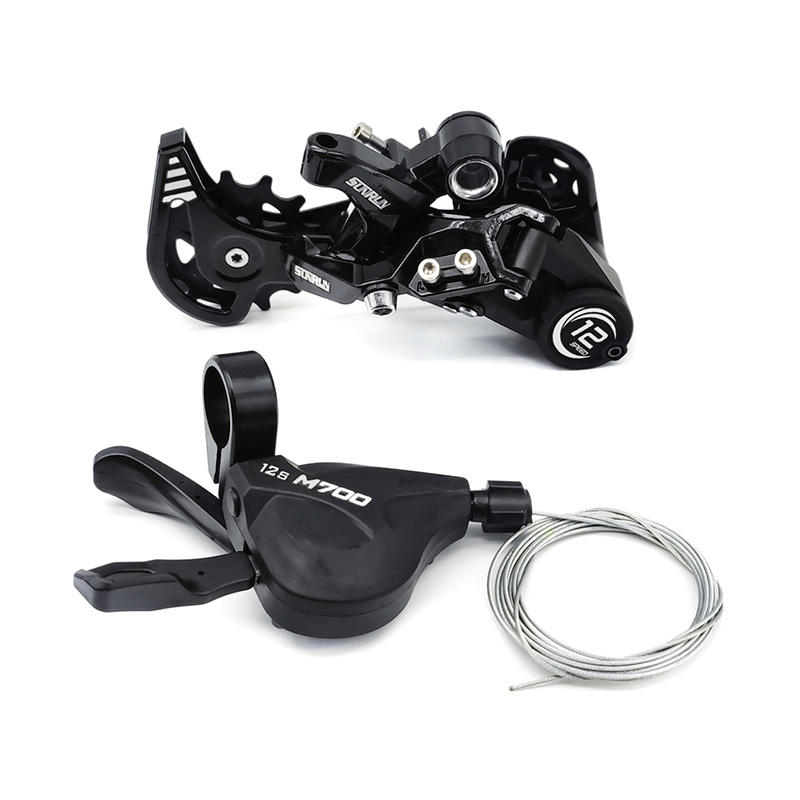
What key role does the front derailleur play in the bicycle speed change process?The front derailleur, also known as the front transmission, is an important part of the bicycle transmission system. It is located above the crankset and fixed to the seat tube of ...
-
 In terms of material selection, what performance advantages do steel and alloy bring to this MTB Bicycle Cassette Sprocket?
In terms of material selection, what performance advantages do steel and alloy bring to this MTB Bicycle Cassette Sprocket?As a metal material, steel has excellent strength and hardness, which makes it an ideal choice for manufacturing MTB Bicycle Cassette Sprockets. During riding, especially on rugged...
-
 How does the Double piston mechanical disc brake set improve the reliability of the brake system?
How does the Double piston mechanical disc brake set improve the reliability of the brake system?The design of the Double piston mechanical disc brake set allows a larger contact area between the brake pad and the brake disc. With two pistons acting at the same time, the brake...

- Describe
- Parameter

Ningbo Dongjin Technology Co., Ltd is China OEM Shifter Transmission Group Set Series Supplier and ODM Shifter Transmission Group Set Series company was founded in 1991, specializing in the production of bicycle transmission systems, braking systems and other components. The leading products include a series of derailleurs, variable speed flywheels, high-end cassette hubs, disc brakes, brake components, cranksets and more than 300 varieties in six categories.
In 2015, in response to Made in China 2025, the company established Ningbo Dongjin Technology Co., Ltd. to develop a new internal and external variable speed transmission system, entering the first echelon of the domestic industry. "Chicheng wheel industry, quality first" is the pursuit of quality by Richeng people. The company has introduced internationally advanced key technologies such as precision cold forging, CNC machining, heat treatment, and multi-station stamping to develop transmissions with Richeng characteristics. , transmission kit, sales volume leads domestic peers. The registered brands SUNRUN, TONGKEEN and HEMU enjoy high reputation in domestic and foreign markets. The company has independent export rights, and its products are exported to Europe, North America, Central and South America, Africa, Southeast Asia and other countries and regions. Xu Mingqiang, chairman of the company, sincerely invites domestic and foreign merchants to come for negotiation and guidance.
Industry Knowledge Extension
Shifter Transmission Group Set Series transmission fault diagnosis and treatment is a complex and critical process involving multiple steps and expertise. Here are the general methods for diagnosing and troubleshooting transmission problems:
1. Fault diagnosis
Symptom recognition:
Pay attention to observe and record the symptoms of transmission failure, such as uneven shifting, abnormal noise, oil leakage, power drop, etc.
Through communication with the driver, understand the specific circumstances and conditions of the failure.
Initial inspection:
Perform a preliminary inspection of the transmission's appearance, connections, oil level, and leaks.
Use diagnostic tools to check the electrical system, including the status of sensors and actuators.
Use diagnostic equipment:
Connect professional diagnostic equipment to the vehicle's diagnostic interface to read the transmission's fault codes and data streams.
Based on the analysis of fault codes and data flows, possible faulty components or systems are located.
Road test and dynamic analysis:
Conduct a road test to observe the transmission's shifting logic, response time and driving stability.
Use diagnostic equipment to record data during the road test and conduct dynamic analysis.
2. Troubleshooting
Replace faulty parts:
According to the diagnosis results, replace faulty sensors, actuators, solenoid valves and other components.
Be sure to use original or quality replacement parts to ensure compatibility with the transmission.
Cleaning and Adjustment:
For failures caused by oil dirt or impurities, clean and adjust the inside of the transmission.
Clean the oil circuit and replace the filter element to ensure that the transmission oil is clean and smooth.
Software updates and calibration:
If the failure is related to transmission software, perform a software update or calibration according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Ensure software compatibility and stability to avoid introducing new problems.
Check mechanical components:
For failures involving mechanical components, such as gears, bearings, etc., disassembly, inspection and repair are performed.
Replace worn or damaged mechanical parts as needed.
3. Subsequent verification
Clear fault code:
After troubleshooting, use diagnostic equipment to clear the transmission's fault codes.
Test again:
Carry out road tests and static tests to verify whether the transmission is back to normal working condition.
Check for other potential faults or problems.
Please note that troubleshooting and troubleshooting of a transmission requires specialized knowledge and experience. If you are not sure how to perform these steps correctly, it is recommended to seek help from a professional technician. Incorrect diagnosis or treatment may result in transmission damage or safety hazards. In addition, regular maintenance and repair of the transmission are also important measures to prevent failures.
 中文简体
中文简体 English
English