-
 Everything You Need to Know About MTB Bicycle Cassette Sprocket
Everything You Need to Know About MTB Bicycle Cassette SprocketWhat is a mountain bike cassette sprocket?A mountain bike cassette sprocket is one of the core components of a mountain bike's speed change system. It is usually installed on the r...
-
 How to properly maintain bicycle hubs with sealed bearings to extend their service life?
How to properly maintain bicycle hubs with sealed bearings to extend their service life?Proper maintenance of bicycle hubs with sealed bearings is the key to ensuring their long-term stable operation. Although the design of sealed bearings can effectively prevent the ...
-
 Bicycle rear derailleur: a key component of riding experience
Bicycle rear derailleur: a key component of riding experienceIn modern bicycle design, the rear derailleur is an indispensable part of the transmission system. It not only bears the heavy responsibility of transferring the chain from the fro...

- Describe
- Parameter

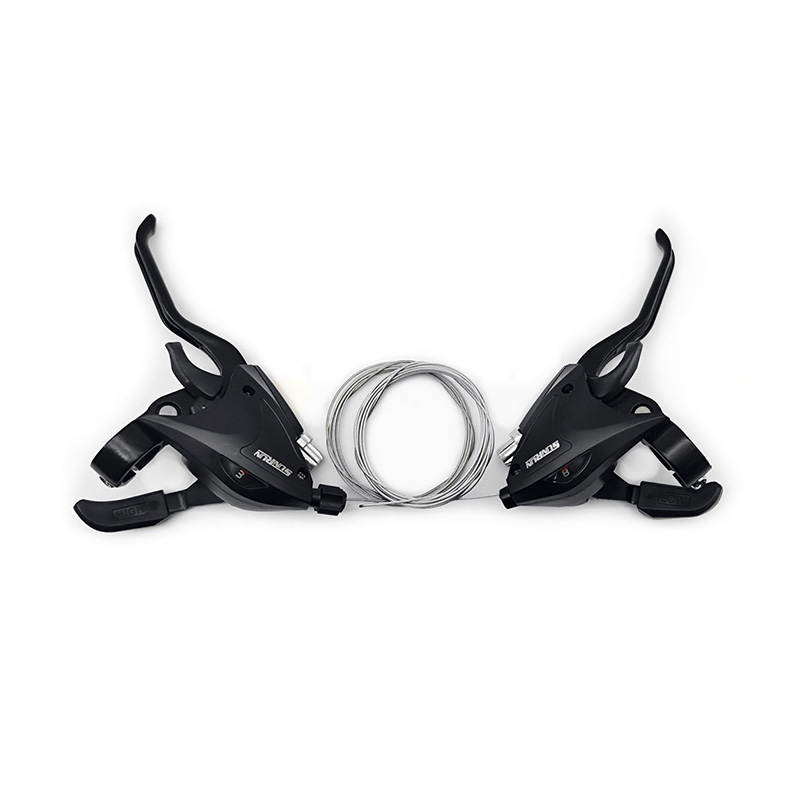
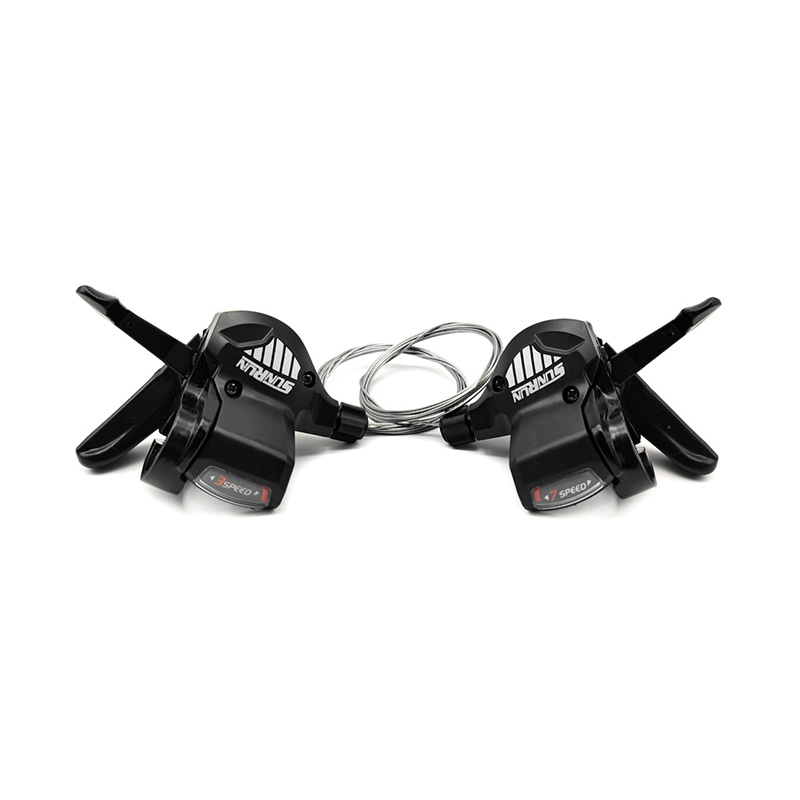
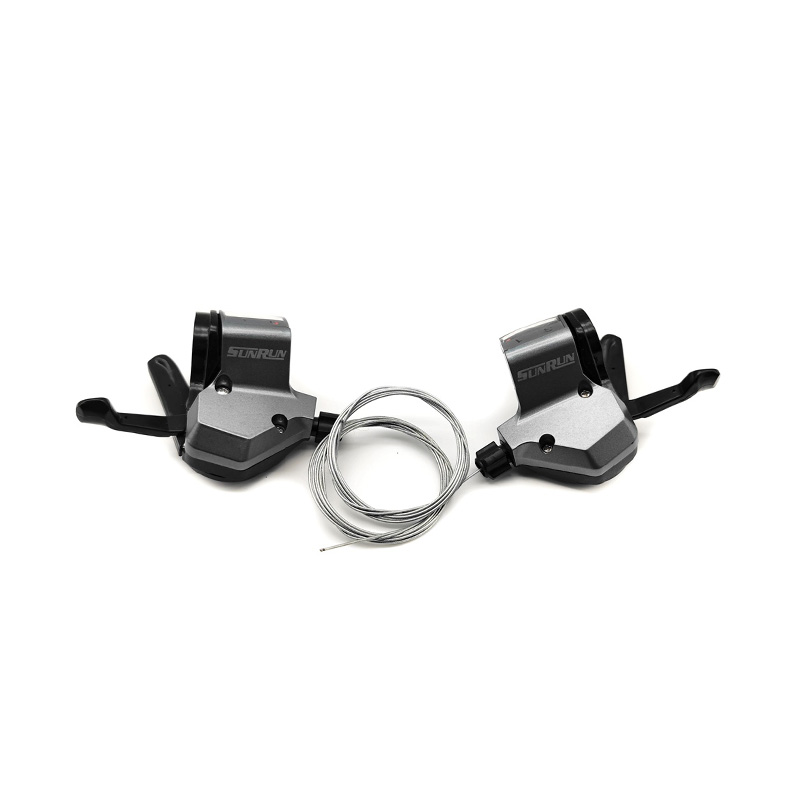
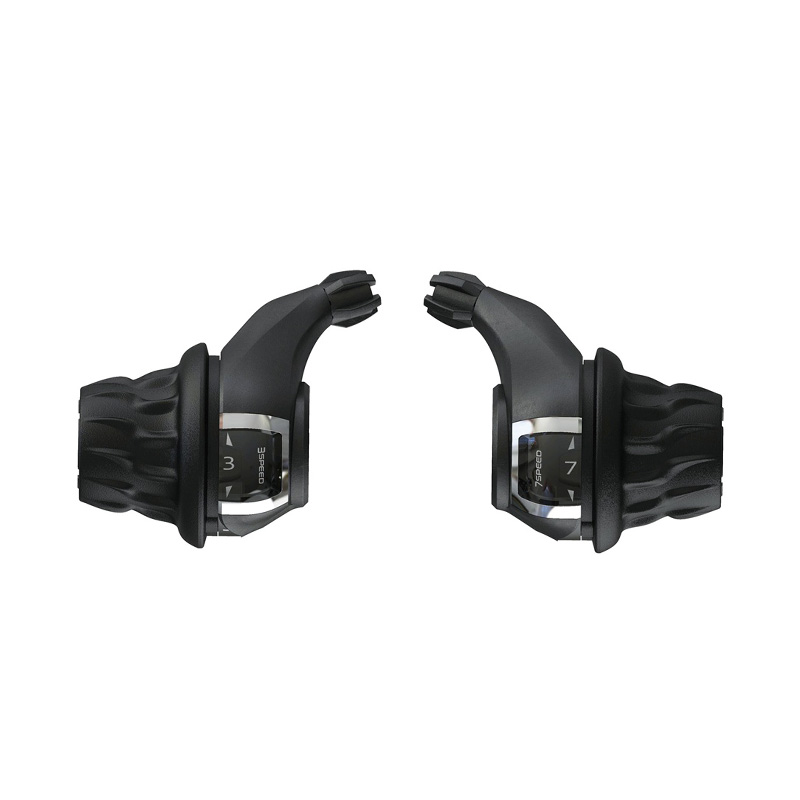
Ningbo Dongjin Technology Co., Ltd is China OEM 3x7S Bicycle Twist Shifter Supplier and ODM 3x7S Bicycle Twist Shifter company was founded in 1991, specializing in the production of bicycle transmission systems, braking systems and other components. The leading products include a series of derailleurs, variable speed flywheels, high-end cassette hubs, disc brakes, brake components, cranksets and more than 300 varieties in six categories.
In 2015, in response to Made in China 2025, the company established Ningbo Dongjin Technology Co., Ltd. to develop a new internal and external variable speed transmission system, entering the first echelon of the domestic industry. "Chicheng wheel industry, quality first" is the pursuit of quality by Richeng people. The company has introduced internationally advanced key technologies such as precision cold forging, CNC machining, heat treatment, and multi-station stamping to develop transmissions with Richeng characteristics. , transmission kit, sales volume leads domestic peers. The registered brands SUNRUN, TONGKEEN and HEMU enjoy high reputation in domestic and foreign markets. The company has independent export rights, and its products are exported to Europe, North America, Central and South America, Africa, Southeast Asia and other countries and regions. Xu Mingqiang, chairman of the company, sincerely invites domestic and foreign merchants to come for negotiation and guidance.
Industry Knowledge Extension
The basic structure of the Bicycle Twist Shifter includes the following main components, and their respective functions are as follows:
Knob (Shifter Lever):
Function: The knob is the part directly operated by the rider. By rotating the knob, the rider can trigger the work of the transmission system. The knob is usually clearly marked to show the different gear positions.
Internal Gear Mechanism:
Function: An internal gear system is responsible for converting the rotary motion of the knob into a pull or release on the shift cable. It usually consists of a series of gears and ratchets that are precisely designed to ensure the accuracy and stability of the rotational action.
Linkage:
Function: The connecting rod connects the knob and the internal gear system to ensure that the rotation of the knob can be accurately transmitted to the internal gear system. It plays the role of transmitting force and movement to ensure the smooth progress of the entire shifting process.
Transmission cable (Derailleur Cable) and its housing (Cable Housing):
Function: The shift cable is responsible for converting the turning motion of the knob into actual operation of the bicycle derailleur. It is connected to the internal gear system on one end and to the transmission's control mechanism on the other. The shift cable housing protects the shift cable from dust and dirt while ensuring the cable slides smoothly.
Cable Tension Adjuster:
Function: The shift cable adjuster is usually located near the knob and is used to fine-tune the tension of the shift cable. It allows the rider to make fine adjustments as needed to ensure accurate and smooth shifting.
These components work together to enable the Bicycle Twist Shifter to achieve the rider's bicycle shifting needs. The rotation of the knob is transmitted to the internal gear system through the connecting rod, which then pulls or releases the shifting cable, ultimately controlling the movement of the guide wheel of the transmission, changing the contact position between the chain and the gear, thereby adjusting the speed and power output of the bicycle. This design makes shifting operations easy and fast, and is suitable for different types of bicycles and riding scenarios.
 中文简体
中文简体 English
English